Coronaviruses (CoV) are a family of viruses that cause illness in humans, ranging from the common cold to severe respiratory syndrome-like Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SAR-CoV).
The novel 2019 coronavirus (COVID-19), which is now officially renamed the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), was identified in Wuhan, China, towards the end of 2019.
It is identified as the 7th member of the coronavirus that affects humans (1). This new virus is spreading person-to-person in 90 countries and territories, of which 80% of cases are in China. It has affected thousands, with a rising death toll of over 3,390 (2).
In this article, we have answered all possible questions about coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Take a look.
Table Of Contents
Coronaviruses are common in both humans and animals. There is a wide range of animals that are known to be the source of coronavirus.
For instance, SAR-CoV was transmitted from civet cats, and MERS-CoV originated from camels (3). However, animal coronaviruses affecting humans are rather rare. Sometimes, coronaviruses that affect animals can be transmitted to humans, evolving into a new coronavirus – like the novel coronavirus – 2019 (4).
Q: How Does COVID-19 Spread? Is It Contagious?
Yes, it is contagious. COVID-19 can spread from person-to-person through respiratory droplets (5). When an infected person coughs or sneezes, if the droplets land in the mouths or noses of people nearby (who are in close contact, within 6 feet), there are high chances of them being exposed to the COVID-19 virus.
One can also be exposed to COVID-19 by coming in contact with a surface or object that has the virus on it. Fortunately, unlike other highly transmissible diseases, this virus cannot remain airborne for long.
Currently, there is no research to confirm its spread through food. Due to its poor survivability, this virus may not spread from food products or other items that are shipped over days or weeks or consumed after long hours.
The incubation period (time between exposure to the virus and the arrival of symptoms) for COVID-19 is estimated between 2-14 days (6).
This virus can spread easily in communities, and for every one infected person, two other people can potentially get the infection if they do not practice hand hygiene and other preventive measures.
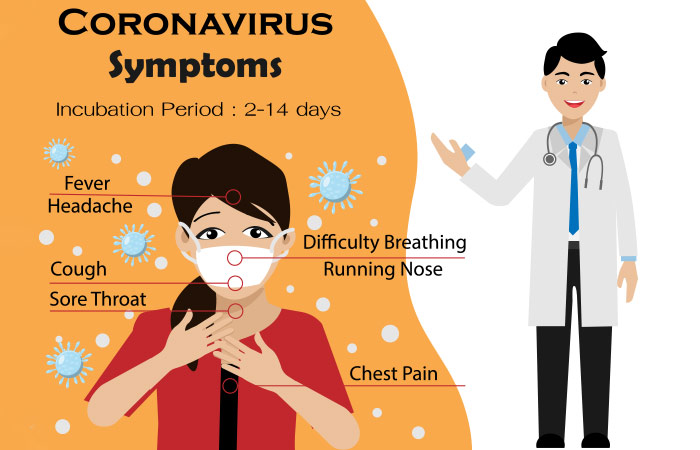
Q: What Are The Symptoms Of COVID-19?
Image: Shutterstock
The current symptoms of this infection are described to have flu-like characteristics. These symptoms may appear 2-14 days after exposure (7).
Call your doctor immediately if you develop these symptoms and have been in contact with an infected person.
If you have traveled from an area that has widespread COVID-19, please visit your doctor immediately.
More critical cases can develop pneumonia-like symptoms, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome. People with a chronic condition are vulnerable to severe illness.
Q: How Is COVID-19 Diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider can determine if your symptoms are explained by other causes or by COVID-19. If the laboratory tests are confirmed, your healthcare provider will collaborate with health officials in your state to collect clinical specimens for diagnosis.
Q: How To Protect Yourself From COVID-19
According to the Centers For Disease Control And Prevention, the best way to steer clear of this virus is by following some basic preventive measures that can control the spread of COVID-19 (8). They include:
Q: What Is The Best Handwashing Technique?
According to the CDC, washing hands regularly can avoid the spread of various diseases.
An effective handwashing technique involves 5 steps (9).
An effective handwashing technique involves 5 steps (9).
If you have spent time in any of the current affected areas:
Q: What Precautions Should People Who Are In Close Contact With A Symptomatic Individual Take?
According to the CDC and WHO, you need to follow these precautions if you are in contact with an affected person (10), (11).
Discuss any additional guidelines with the respective healthcare provider
Q: What Treatments Are Available For COVID-19?
According to the Centers For Disease Control And Prevention, currently, there is no specific treatment for COVID-19. People with COVID-19 should receive immediate care to help manage the symptoms.
If you think you are exposed to COVID-19, visit your healthcare provider immediately. For severe cases of COVID-19, treatments include high-intensity support to vital organ functions. Firsthand treatment includes immediate isolation and the implementation of appropriate infection prevention and control (IPC) measures (8).
Q: How Long Does COVID-19 Last?
Most people affected with COVID-19 may recover within 2-3 weeks. However, the recovery time varies from person-to-person, depending on their immunity levels. People with pneumonia take longer to recover. In critical cases, it may take months to recover, or the person may die.
Q: Will Heat Kill COVID-19?
It is thought that COVID-19 can survive for up to four days on surfaces. Some researchers say that the survivability of these viruses might be reduced during the summer. However, there is currently no data on how heat can affect the virus (12).
The CDC does not recommend healthy people to wear a face mask to protect themselves from COVID-19. If you are not infected, you need not wear a mask. You only need to wear a mask if you are taking care of an infected person. The purpose of a face mask is to prevent the spread of the disease to others.
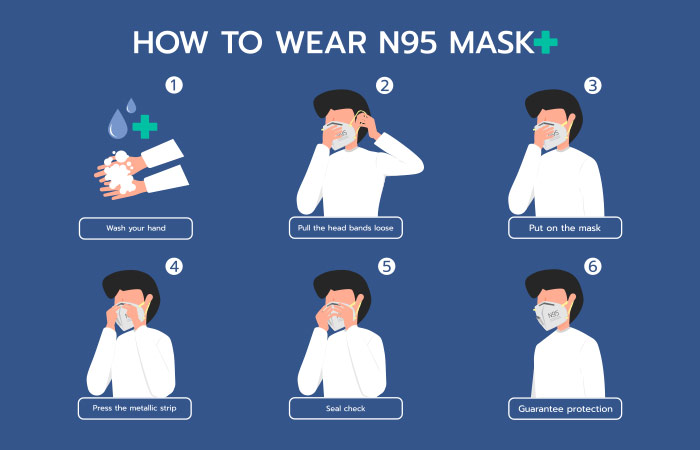
Q: How To Put On A Mask?
Image: Shutterstock
The World Health Organisation estimates 3.4% mortality rate as of March 3, 2020 (13).
Q: COVID-19 In Babies – Are Children At Risk?
There is no evidence that children are at risk of this virus (14). Most confirmed cases, as of now, are seen in adults. Very few young children have been reported to have COVID-19. However, to be on the safe side, children are advised to practice general preventive measures.
Q: Which Age Group Is At Increased Risk?
According to the WHO, medium-aged people are at higher risk of contracting COVID-19 (15). Very few cases are detected among children below 10 years.

This post have 0 komentar
EmoticonEmoticon